The Board of Governors is the supervisory body of the Federal Reserve System. It consists of seven individuals appointed by the President and approved by Congress. Each individual serves a term of 14 years. These terms are staggered to provide continuity, with a new member being appointed every two years. The positions of Chairman and Vice-Chairman are decided by the President and last a duration of four years. Consecutive terms are possible. The primary function of the Board is to establish a monetary policy that will promote the economic goals of the country. The Governors and their policies are accountable to the Congress.The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), made up of twelve members, serves as the Reserve's main policy making body. It includes the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the New York Federal Reserve Bank, and four other Federal Reserve Bank presidents that rotate membership on a one year basis. The committee establishes open market policy and conducts open market operations. These activities determine the amount of money and the availability of credit in the U. S. economy.
The Federal Advisory Council is a group of twelve representatives, one from each of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts. The Council meets four times a year and offers its advice to the Board of Governors.
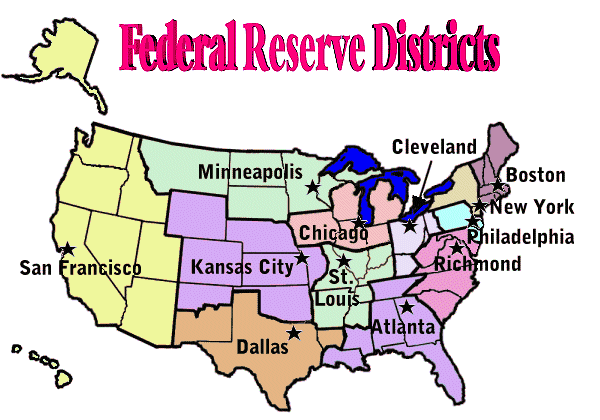
The twelve Federal Reserve Districts impliment the policies established by the Open Market Committee. Each Federal Reserve Bank provides services for the commercial banks of its district.